Contacts:
Alan MacRobert, Senior Editor
855-638-5388 x2151, [email protected]
J. Kelly Beatty, Senior Contributing Editor
617-416-9991, [email protected]
Note to Editors/Producers: This release is accompanied by high-quality illustrations; see end of release.

This animation shows the trajectory of asteroid 2005 YU55 as it cruises past Earth on the night of November 8-9, 2011.
NASA / JPL
Earth is about to be visited by the largest close-approaching asteroid on record. Known as 2005 YU55, it is about a quarter mile (400 m) across, round, and quite dark. When it comes closest to us, at 6:28 p.m. EST (23:28 Universal Time) on November 8th, it will be 198,000 miles (319,000 km) from Earth's surface — closer than the Moon's orbit. Professional astronomers around the world will closely follow the asteroid as it glides across the sky.
Weather permitting, backyard skywatchers also have a chance to spot this interloper. A few hours after passing closest to us, it will peak in brightness at magnitude 11.1, roughly 100 times fainter than the limit of human vision. "The good news," says Alan MacRobert of Sky & Telescope magazine, "is that you should be able to spot the asteroid with your telescope if it has an aperture of at least 6 to 8 inches."
The asteroid's track past Earth is especially favorable for western Europe and North America. But you'll need to know exactly where and when to look: the object will traverse the 70° of sky eastward across several constellations, from Aquila to Pegasus, in just 10 hours. At times it will zip among the background stars at 7 arcseconds per second, covering a Moon's width of sky in under 5 minutes. And light from a nearly full Moon will brighten the entire sky somewhat, making faint stars and the asteroid somewhat more difficult to spot.
To determine where to look, Sky & Telescope's editors have prepared two detailed finder charts. The first gives a general sense of where to look, and the second provides a detailed view to use while outside with your telescope. Once you've aimed at exactly the right spot, you shouldn’t have much trouble telling which starlike point is 2005 YU55. It will be gliding fast enough to move along in real time as you watch using a moderately high-magnification eyepiece.
"As it passes Earth, the asteroid gets so close that its position among the stars will be significantly affected by your location," explains MacRobert. So the magazine's detailed finder chart takes this parallax effect into account, by including small upside-down maps of the United States that permit you to establish the correct path for your location.
Discovered nearly six years ago by Robert McMillan at Steward Observatory's Spacewatch Telescope in Arizona, 2005 YU55 has been this way before. In April 2010, it ventured close enough for detailed radar probing by the giant radio dish at Arecibo, Puerto Rico.
Professional astronomers have recruited advanced backyard amateurs to do precision brightness measurements of the asteroid during its flyby (more information is here).
Sky Publishing (a New Track Media company) was founded in 1941 by Charles A. Federer Jr. and Helen Spence Federer, the original editors of Sky & Telescope magazine. In addition to Sky & Telescope and SkyandTelescope.com, the company publishes two annuals (Beautiful Universe and SkyWatch), as well as books, star atlases, posters, prints, globes, and other fine astronomy products.
Permission is granted for nonexclusive use of the illustrations in any media as long as credit is given to Sky & Telescope magazine. Web publication must include a link to http://SkyandTelescope.com.
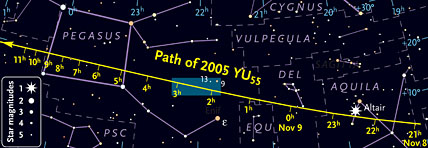
Best seen from North America, the little asteroid 2005 YU55 will race far across the constellations in just 11 hours on the night of November 8-9, 2011. Click on the image for a more detailed chart.
Sky & Telescope illustration
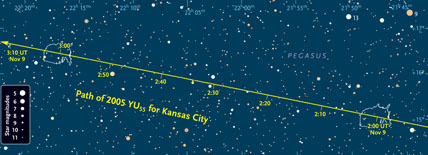
The path of the asteroid 2005 YU55 is plotted for just over an hour on the evening of November 8th for North America, from 1:51 to 3:12 Universal Time on November 9th. (To convert Universal Time to your time zone, subtact 5 hours for EST, 6 for CST, 7 for MST, and 8 for PST.) North is up; east is left. On each of the little upside-down maps of the U.S., put a pencil dot on your location. These are the asteroid”™s apparent positions at 2:00 and 3:00 UT for your site. Connect your dots with a straight line paralleling the line plotted, which is for Kansas. Click on the image for a high-resolution version; click here for a high-resolution version with black stars on a white background.
Sky & Telescope illustration
 0
0
Comments
You must be logged in to post a comment.